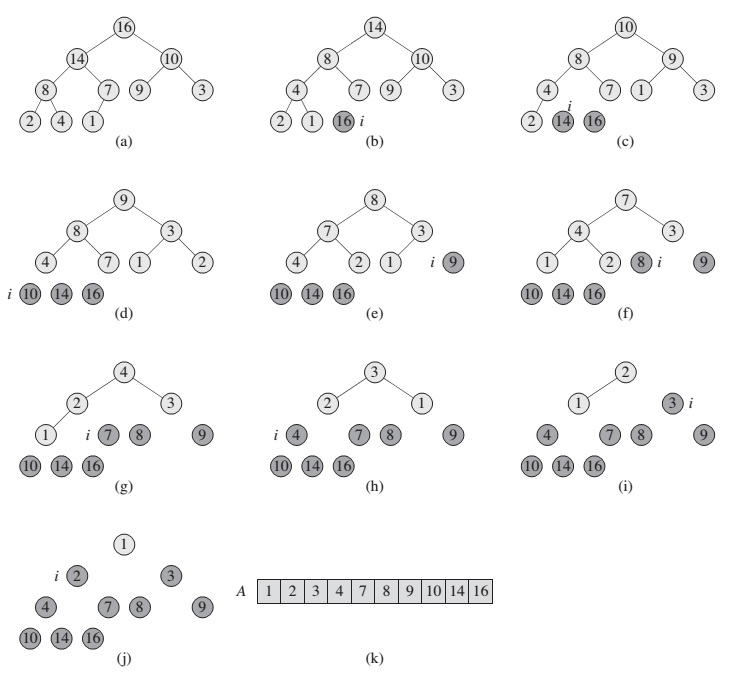
Heapsort#
Definition#
A heap`` is a specialized binary tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property. In the context of sorting, a heap`` usually refers to a binary heap. A binary heap is a complete binary tree where the parent node’s value is either greater than or less than its children, depending on whether it’s a max-heap or a min-heap. In the case of heap sort, a max-heap is often used, where the largest element is at the root.

Advantages & Disadvantages#
\(O(n * log(n))\)
making it efficient for large datasets
In-place sorting
doesn’t require additional memory
Not stable
Equal elements can be rearranged during the sorting process
Slower
…for small datasets compared to some other sorting algorithms.
\(O(n * log(n))\)
Worst / Average Case complexity the same…
Programming#

HeapSort(arr):
BuildMaxHeap(arr) // Build a max heap from the array.
for i from n down to 2: // n is the size of the array.
Swap arr[1] and arr[i] // Move the maximum element to the end.
Heapify(arr, 1, i-1) // Restore the max-heap property.
BuildMaxHeap(arr):
for i from n/2 down to 1:
Heapify(arr, i, n)
Heapify(arr, i, n):
largest = i
left = 2 * i
right = 2 * i + 1
if left ≤ n and arr[left] > arr[largest]:
largest = left
if right ≤ n and arr[right] > arr[largest]:
largest = right
if largest ≠ i:
Swap arr[i] and arr[largest]
Heapify(arr, largest, n)
1#include <iostream>
2
3// Function to heapify a subtree rooted at index i.
4void heapify(int arr[], int n, int i) {
5 int largest = i;
6 int left = 2 * i + 1;
7 int right = 2 * i + 2;
8
9 if (left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest])
10 largest = left;
11
12 if (right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest])
13 largest = right;
14
15 if (largest != i) {
16 std::swap(arr[i], arr[largest]);
17 heapify(arr, n, largest);
18 }
19}
20
21// The main function to perform heap sort.
22void heapSort(int arr[], int n) {
23 // Build a max-heap.
24 for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
25 heapify(arr, n, i);
26
27 // Extract elements one by one from the heap.
28 for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
29 std::swap(arr[0], arr[i]); // Move current root to end.
30 heapify(arr, i, 0); // Call max heapify on the reduced heap.
31 }
32}
33
34int main() {
35 int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
36 int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
37
38 heapSort(arr, n);
39
40 std::cout << "Sorted array is: ";
41 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
42 std::cout << arr[i] << " ";
43
44 return 0;
45}
Real World Use Cases#
Heap sort may not be directly used in real-world applications, but the heap data structure itself has various applications. For example:
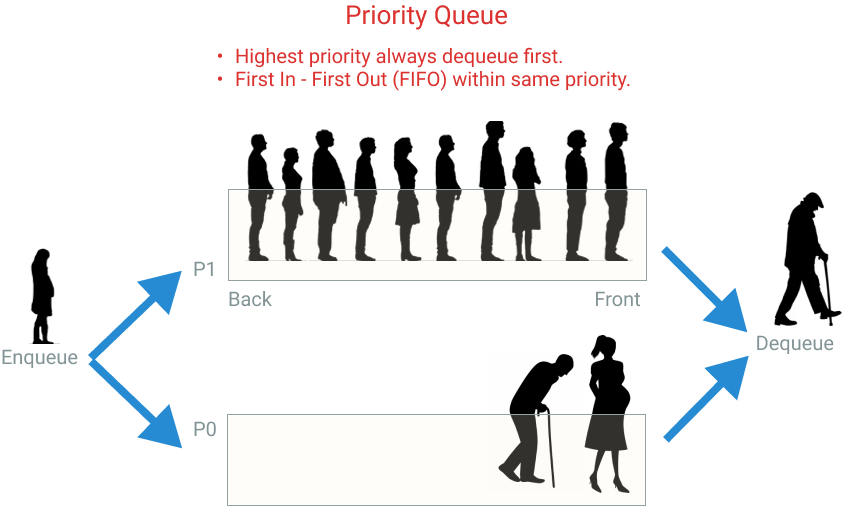
- Priority Queues
Heaps are used to efficiently implement priority queues, which are essential in various scheduling algorithms and simulations.
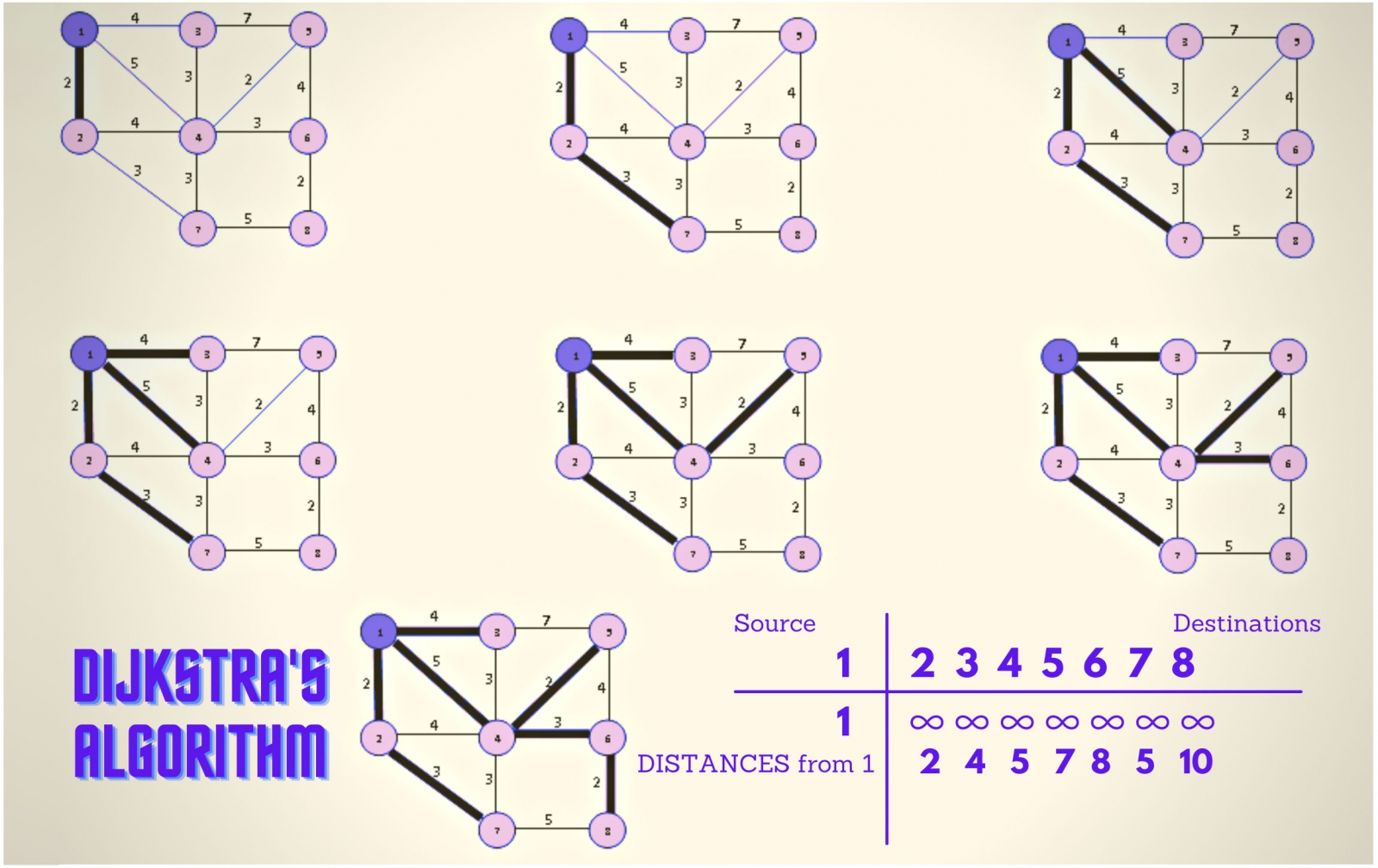
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
It employs a min-heap to find the shortest path in a graph.
- Memory Management
Heaps are used in memory management systems to allocate and de-allocate memory efficiently.