Stacks#
A stack is a linear data structure in computer science that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle. In simpler terms, the element that is added last to the stack is the first element to be removed from it.
A stack is similar to a stack of books, where the book that is placed on top is the first book to be removed. The stack data structure has two primary operations: push and pop. The push operation adds an element to the top of the stack, while the pop operation removes the topmost element from the stack.
Stacks are commonly used in programming for various purposes, such as function calls, expression evaluation, and memory allocation. In function calls, a stack is used to keep track of the sequence of function calls that are made during the execution of a program. In expression evaluation, a stack is used to evaluate arithmetic expressions, such as infix, postfix, and prefix expressions. In memory allocation, a stack is used to allocate and de-allocate memory for variables and data structures.
Documentation#
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::stack<int> s;
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
std::cout << s.size() << " elements on stack\n";
std::cout << "Top element: " << s.top() << "\n";
std::cout << s.size() << " elements on stack\n";
s.pop();
std::cout << s.size() << " elements on stack\n";
std::cout << "Top element: " << s.top() << "\n";
return 0;
}
3 elements on stack
Top element: 3
3 elements on stack
2 elements on stack
Top element: 2
Basic Operations#

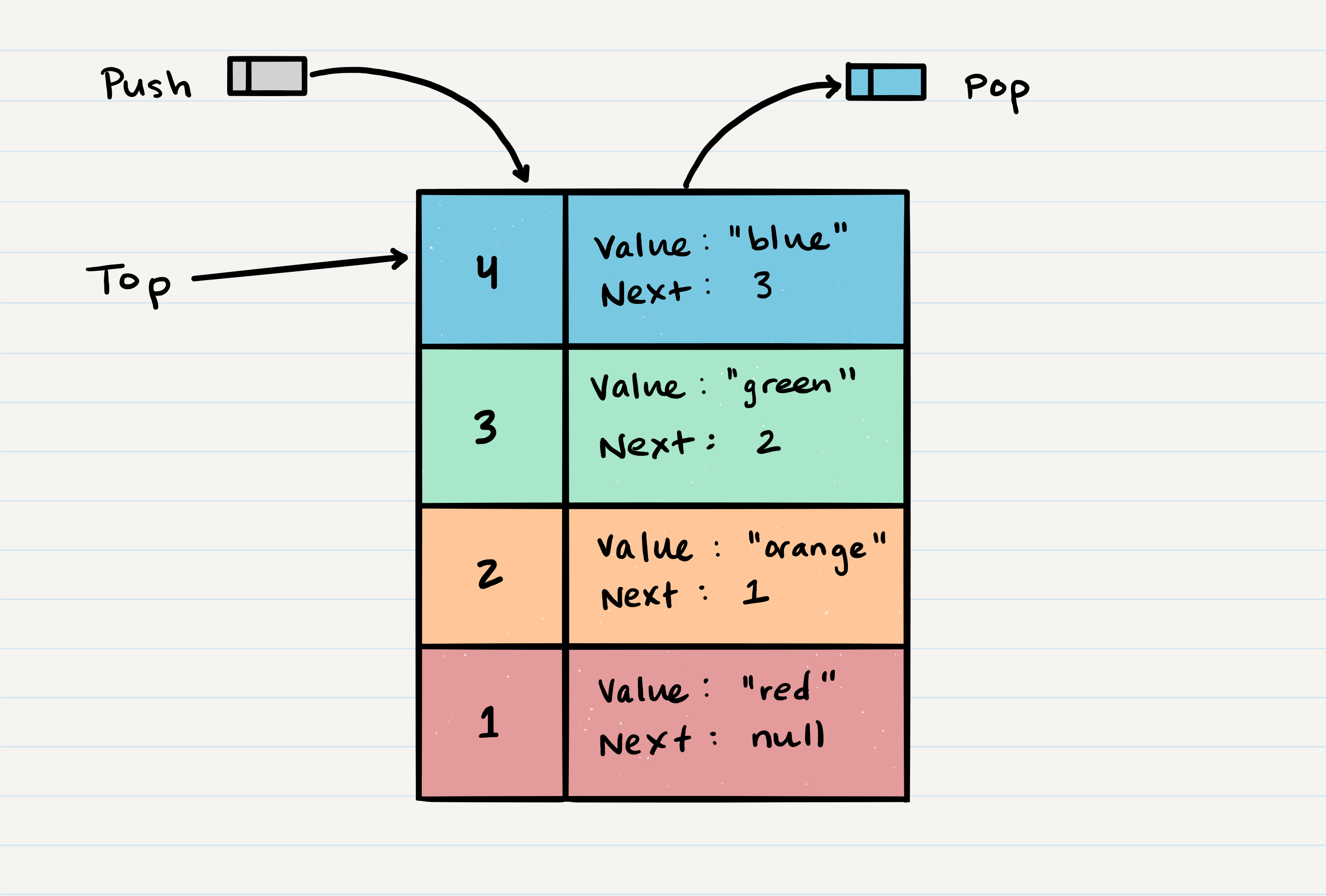
push
Built-in Function
inserts one element onto the stack

A new item can be pushed into a stack using the following steps
Check if the stack is full. If it is, then you can not insert the item. Raise “Stack Overflow” error.
If the stack is not full, insert the item at the top of the stack.
Make this item a new top of the stack.
pop
Built-in Function
returns the element at the top of the stack (and removes it)

- An item on the top of the stack can be removed (popped) using following steps.
Check if the stack is empty. If it is, then you can not remove the item. Raise “Stack Underflow” error.
If the stack is not empty, remove the item at the top of the stack.
Update the top of the stack.
push-pop

Fig. 9 For levity…#
isEmpty
Built-in Function
not necessary, but sometimes useful
The
topoperation returns the item at the top of the stack. Don’t be confused this operation with thepopoperation. Thepopoperation removes the top item whereas thetopoperation only reads the value of the top item. As in thepopoperation, we need to check if the stack is empty before reading the value.
Implementation : Array#
Flow Chart Sample

Arrays
push and pop at the end of the array (easier and efficient)
can be fixed-length
can also use a dynamic array (grows overtime)
additional cost for dynamic arrays

Stack
class Stack {
private:
int *array;
int length;
int top_idx;
public:
Stack();
~Stack();
void push(int);
int peek(); // returns top
void pop(); // removes top
}
Stack: Array Sample
// CPP program to illustrate
// Implementation of push() function
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Empty stack
stack<int> mystack;
mystack.push(0);
mystack.push(1);
mystack.push(2);
// Printing content of stack
while (!mystack.empty()) {
cout << ' ' << mystack.top();
mystack.pop();
}
}
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-push-and-pop-in-c-stl/?ref=rp
Visualize: Stack Array (general premise)
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/StackArray.html
Visualize: Stack Array (in Memory)
May take a few seconds to load…
Implementation : Linked List#
Linked Lists
push and pop at front (could use the other end as well)

Stack: LL Sample
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int data) {
this->data = data;
next = NULL;
}
};
class Stack {
private:
Node* top;
public:
Stack() {
top = NULL;
}
void push(int data) {
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->next = top;
top = newNode;
}
int pop() {
if (top == NULL) {
return -1; // stack is empty
}
int popped = top->data;
Node* temp = top;
top = top->next;
delete temp;
return popped;
}
int peek() {
if (top == NULL) {
return -1; // stack is empty
}
return top->data;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return top == NULL;
}
};
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int data) {
this->data = data;
next = NULL;
}
};
class Stack {
private:
Node* top;
public:
Stack() {
top = NULL;
}
};
void push(int data) {
Node* newNode = new Node(data);
newNode->next = top;
top = newNode;
}
int pop() {
if (top == NULL) {
return -1; // stack is empty
}
int popped = top->data;
Node* temp = top;
top = top->next;
delete temp;
return popped;
}
int peek() {
if (top == NULL) {
return -1; // stack is empty
}
return top->data;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return top == NULL;
}
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implement-a-stack-using-singly-linked-list/
Visualize: Stack Array (general premise)
Visualize: Stack LL (in Memory)
May take a few seconds to load…
Considerations#
-27856afe-5df2-45ee-afdb-59af2e1629c1.jpg)
Underflow
error can be thrown when calling pop on an empty stack
Overflow
error can be thrown when calling push on a full stack (especially in fixed-length implementations)
Applications#
Undo in software applications…
Stack in compilers/programming languages…
Parsing expressions…
etc…
Time & Space Complexity#
Operation |
Best Case |
Worst Case |
Average Case |
Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|
\(push()\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(\color{red}{O(n)}\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(pop()\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(peek()\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
\(O(1)\) |
