Search Algorithms#
Search algorithms are a fundamental concept in data structures and algorithms that are used to find an item in a collection of data. There are several types of search algorithms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Linear search is a simple search algorithm that examines each element in a collection until the desired item is found. Linear search is easy to implement and works well for small collections or unsorted data, but it can be inefficient for large collections or when the desired item is near the end of the collection.
Binary search is a more efficient search algorithm that works on sorted collections. Binary search divides the collection in half at each step and eliminates one half of the remaining items based on the comparison with the target value. Binary search has a time complexity of \(O(log\ n)\), making it much faster than linear search for large collections.
Hashing is another search algorithm that works by using a hash function to map the search key to an index in an array. Hashing provides fast access to items with a time complexity of \(O(1)\), but it requires a good hash function and can suffer from collisions where multiple items map to the same index.
Tree-based search algorithms, such as binary search trees and balanced trees, provide efficient search operations with time complexity of \(O(log\ n)\). They are particularly useful for data that needs to be sorted, and can also be used for other operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal.
The choice of search algorithm depends on the properties of the data and the specific requirements of the application. By choosing the most appropriate search algorithm, programmers can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their programs.

Binary Search
repeatedly target the center of the search structure and divide the search space in half.
ex. binary search
note: specifically designed for searching in sorted data-structures…
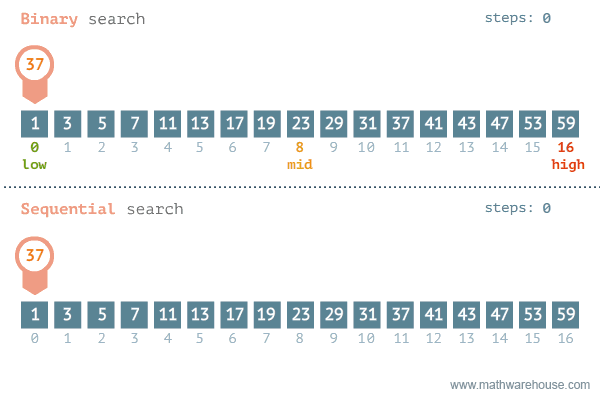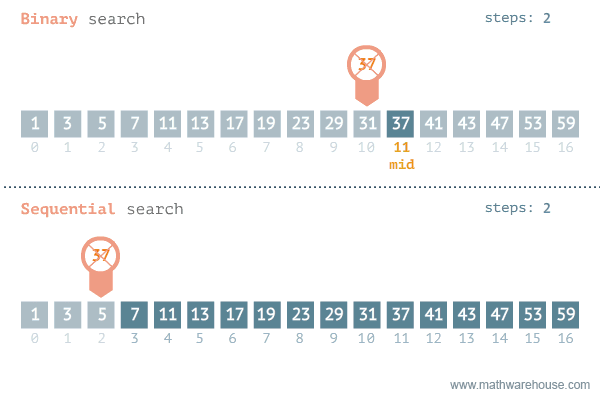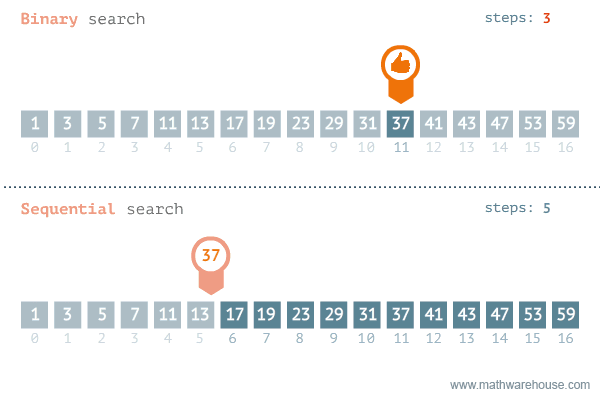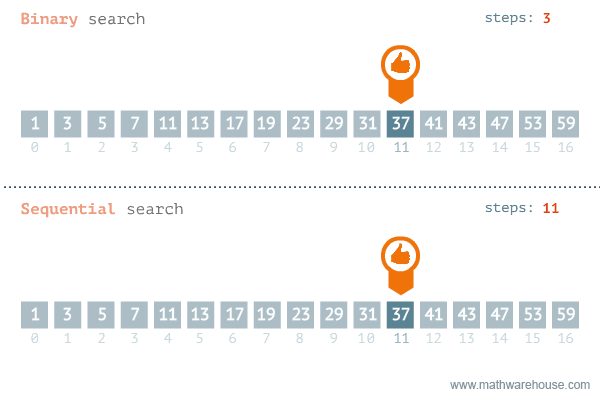
Sequential Search
the list or array is traversed sequentially and every element is checked.
ex. linear search
Linear Search#

https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/images/linear_search.gif
Linear Search: Implementation
// Pseudocode
// -
// Iterate from 0 to N-1,
// compare the value of every index with x
// if they match, return index
### <b>
int linearSearch(int array[], int n, int x) {
// Going through array sequencially
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] == x) return i;
return -1;
}
Rules
Consider all possible cases.
Find the number of comparisons for each case.
Add the number of comparisons and divide by the number of cases.
Best-case \( \Rightarrow T(n) = O(1)\)
Worst-case \( \Rightarrow T(n) = O(n)\)
Average-case (in a successful search) \( \Rightarrow T(n) = O(n)\)
Binary Search#
Pseudocode#
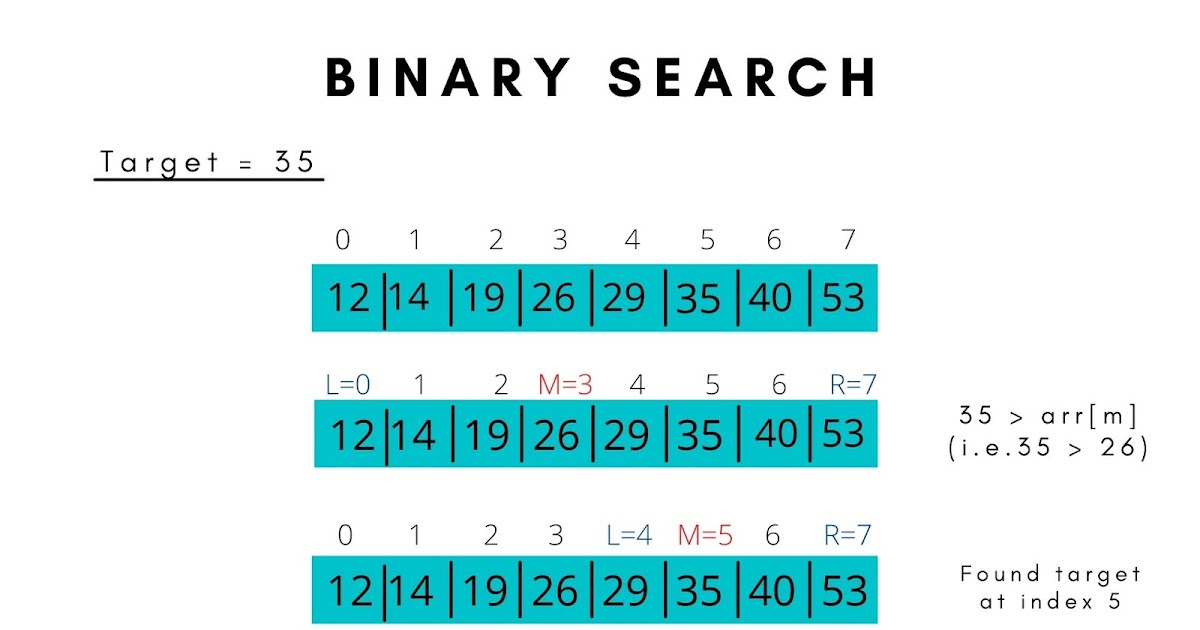
Consider start index to be at \(0\) and last index to be
n-1index at starting\(n \rightarrow length\)
Find middle index
midof the arrayIf
keyis found to be less thanmidindex element then update last index of the array tomid- 1Else if
keyis found to be greater thanmidindex element then update start index of the array tomid+ 1Else check for
midindex element withkeyif not match repeat the above steps tilstartindex is less thanendindex
If
startis less thanendperform Binary search else terminate the algorithm.If the element at
mid(middle index) is equal to thekeythen return the index as it found the keyElse if the
keyis less thanmid(the element middle index) then call the function by passing end asmid- 1 (askeywill be less thanmidelement)Else if the
keyis greater thanmidthen call the function by passing start asmid+ 1 (askeywill be greater thanmid)
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/linear-search-vs-binary-search/?ref=rp
https://takeuforward.org/data-structure/binary-search-explained/
Binary Search#
iterative
int binarySearch(int array[], int x, int low, int high) {
// Repeat until the pointers low and high meet each other
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (array[mid] == x) return mid;
if (array[mid] < x) low = mid + 1;
else high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
visualize: iterative
recursive
int binarySearch(int arr[], int start, int end, int k) {
if (start > end) return -1;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (k == arr[mid]) return mid;
else if (k < arr[mid]) return binarySearch(arr, start, mid - 1, k);
else return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, end, k);
}
visualize: recursive
Analysis#
Rules
Break down the problem into sub-problems
Solve the sub problems
Merge the sub problems to get desired Output
Note: Must be sorted
Best-case \( \Rightarrow T(n) = O(1)\)
Worst-case \( \Rightarrow T(n) = O(log\ n)\)
Average-case (in a successful search) \( \Rightarrow T(n) = O(log\ n)\)
Linear v. Binary#
Linear |
Binary |
|---|---|
Input data need not to be in sorted. |
Input data need to be in sorted order. |
Also called sequential search. |
Also called half-interval search. |
\(T(n) = O(n)\) |
\(T(n) = O(log\ n)\) |
Multidimensional array can be used |
Only single dimensional array is used |
Performs equality comparisons |
Performs ordering comparisons |
Less complex. |
More complex. |
Very slow process. |
Very fast process. |
