MTH 180 Concepts#
Additional Resources
The following sets of videos have been vetted for the general knowledge of mathematical subject matter applicable to CSC 212 but not directly focused on. This is not an exhaustive list, but a guide to helpful instruction. The variety in selection is merely to help fit the multitude of learning curves for students within the course.
Introduction to Sequences : 53:35
Arithmetic Sequences : 21:31
Arithmetic Series : 15:11
Geometric Sequences : 30:14
Geometric Series : 42:02
Proof by Mathematical Induction : 22:35
Sequence and Series | Terms of Sequence and Associated Series | Pre-Calculus : 11:46
Properties of Sigma Notation and Summation Formulas | Pre-Calculus : 11:18
Evaluating Sigma Notation | Summation Formulas | Pre-Calculus : 7:47
Writing Summations in Sigma Notation | Series and Sigma Notation | Pre-Calculus : 10:37
Proof by Mathematical Induction | Principle of Mathematical Induction | Sample Problems | Part 1 : 13:23
Proof by Mathematical Induction | Part 3 | Pre-Calculus : 12:37
Proof by Mathematical Induction | Part 4 | Pre-Calculus : 8:00
Sequences#
- Sequence#
a function whose domain is the set of positive integers
ex: \(\{ 1, 2, 3, 4, \dots \}\)
The general, or \(n^{th}\) term, is denoted as \(a_n\)
\(odd\ integers\) |
\(1\) |
\(3\) |
\(5\) |
\(7\) |
\(9\) |
\(\dots\) |
\(n\) |
\(perfect\ squares\) |
\(1\) |
\(4\) |
\(9\) |
\(16\) |
\(25\) |
\(\dots\) |
\(n\) |
\(a_1\) |
\(a_2\) |
\(a_3\) |
\(a_4\) |
\(a_5\) |
\(\dots\) |
\(a_n\) |
Try it
Write out the first five (5) terms of the sequence…
\(a_n = 2n + 3\)
\(a_n = (-1)^n * \frac{6 - 2n}{ \sqrt{n + 1}} \)
Try it
Write the \(n^{th}\) term of the sequence \(\{a_n\}\) suggested by the pattern
\(\frac{2}{3}, \frac{4}{9}, \frac{8}{27}, \frac{16}{81}, \dots \)
Find the pattern…
\(\frac{2^1}{3^1}, \frac{2^2}{3^2}, \frac{2^3}{3^3}, \frac{2^4}{3^4} \)
Therefore,
\( 2, -4, 6, -8, 10, \dots \)
Find the pattern…
\(2\) |
\(-4\) |
\(6\) |
\(-8\) |
\(10\) |
\(\dots\) |
\(n\) |
\(a_1\) |
\(a_2\) |
\(a_3\) |
\(a_4\) |
\(a_5\) |
\(\dots\) |
\(a_n\) |
Therefore,
- Recursive relation#
a sequence for which the given is the first term together with a rule for obtaining any \(a_{n+1}\) from the preceding term \(a_n\) for \(n \ge 1\)
Try it
Find the first five (5) terms of the recursively defined infinite sequence
\(a_1 = 2, \ \ \ \ \ a_{n+1} = - \frac{n}{a_n}\)
\(a_1 = -1, \ \ \ \ \ a_2 = 1, \ \ \ \ \ a_n = a_{n+1} + na_{n-1}\)
Series#
- Series#
the sum of a number of terms in a sequence
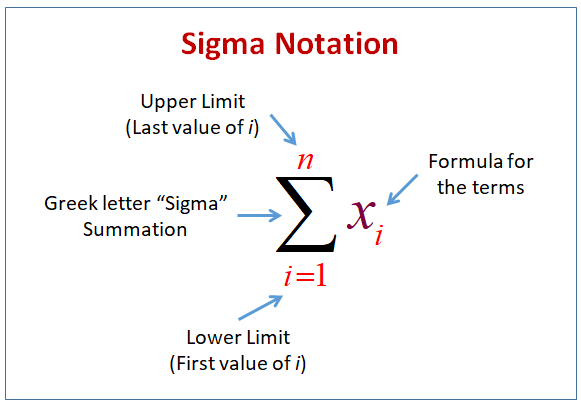
\(n\) = stopping point
\( \sum \) = \(sigma\) or “sum of”
\(k\) = starting point
\(a_k\) = formula for each term
Example
Try it
Write out each sum (expand and simplify)
\( \sum_{k=1}^{6} \frac{3}{k+1} \)
Try it
Express each sum using summation notation
\( 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + \dots + [2(12)-1] \)
Try it
Find the sum for each sequence
\( \sum_{k=1}^{24} -k \)
Formula
\( \sum_{k=137}^{428} 2.1 \)
Formula
\(c\) = constant
\( \sum_{k=0}^{14} k^2-4 \)
Formula
Breakout 1
Breakout 2
Outcome
