Trees#
a tree is a data structure that represents a hierarchical structure. It is composed of nodes connected by edges, with each node containing a value and zero or more child nodes. The topmost node in the tree is called the root node, while nodes that have no children are called leaf nodes.
There are many different types of trees, including binary trees, AVL trees, and red-black trees, each with its own set of rules and constraints. Trees can be used to represent a variety of data structures, including file systems, abstract syntax trees, and search trees.
Trees are an important data structure in computer science because they provide efficient access and manipulation of data. For example, search trees can be used to efficiently store and retrieve large amounts of data, while binary trees can be used to implement sorting algorithms such as heapsort.
Overall, trees are a powerful tool for organizing and managing complex data structures in computer science.
What is a tree?#
A tree data structure is a hierarchical structure that is used to represent and organize data in a way that is easy to navigate and search. It is a collection of nodes that are connected by edges and has a hierarchical relationship between the nodes.
The topmost node of the tree is called the root, and the nodes below it are called the child nodes. Each node can have multiple child nodes, and these child nodes can also have their own child nodes, forming a recursive structure.
– gfg
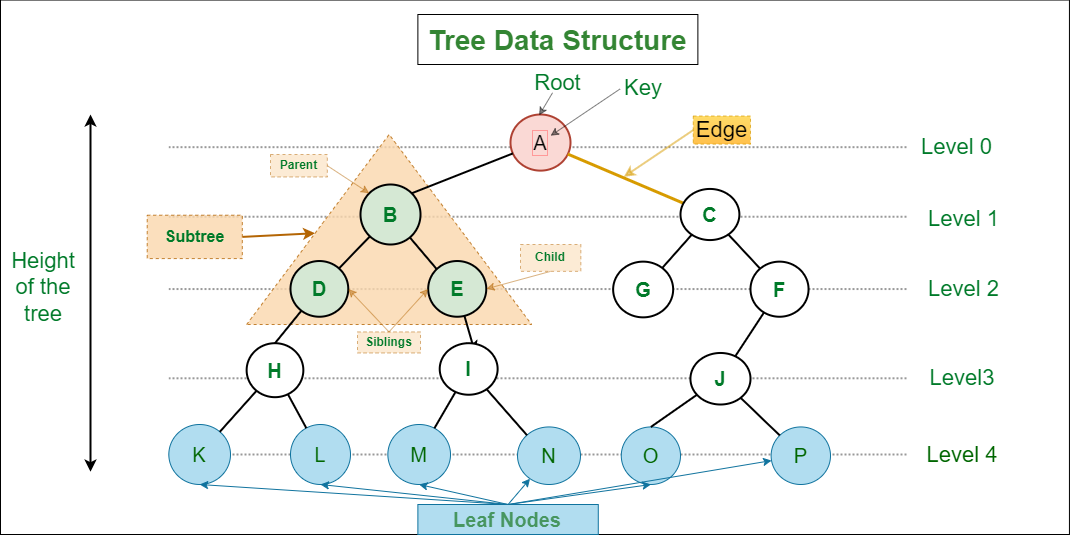
Fig. 13 Anatomy of a Tree#
Terminology#
- Parent Node#
The node which is a predecessor of a node is called the parent node of that node. {B} is the parent node of {D, E}.
- Child Node#
The node which is the immediate successor of a node is called the child node of that node. Examples: {D, E} are the child nodes of {B}.
- Root Node#
The topmost node of a tree or the node which does not have any parent node is called the root node. {A} is the root node of the tree. A non-empty tree must contain exactly one root node and exactly one path from the root to all other nodes of the tree.
- Leaf Node or External Node#
The nodes which do not have any child nodes are called leaf nodes. {K, L, M, N, O, P} are the leaf nodes of the tree.
- Ancestor of a Node#
Any predecessor nodes on the path of the root to that node are called Ancestors of that node. {A,B} are the ancestor nodes of the node {E}
- Descendant#
Any successor node on the path from the leaf node to that node. {E,I} are the descendants of the node {B}.
- Sibling#
Children of the same parent node are called siblings. {D,E} are called siblings.
- Level of a node#
The count of edges on the path from the root node to that node. The root node has level 0.
- Internal node#
A node with at least one child is called Internal Node.
- Neighbor of a Node#
Parent or child nodes of that node are called neighbors of that node.
- Subtree#
Any node of the tree along with its descendant.
Properties#
- Number of edges#
An edge can be defined as the connection between two nodes. If a tree has N nodes then it will have (N-1) edges. There is only one path from each node to any other node of the tree.
- Depth of a node#
The depth of a node is defined as the length of the path from the root to that node. Each edge adds 1 unit of length to the path. So, it can also be defined as the number of edges in the path from the root of the tree to the node.
- Height of a node#
The height of a node can be defined as the length of the longest path from the node to a leaf node of the tree.
- Height of the Tree#
The height of a tree is the length of the longest path from the root of the tree to a leaf node of the tree.
- Degree of a Node#
The total count of subtrees attached to that node is called the degree of the node. The degree of a leaf node must be 0. The degree of a tree is the maximum degree of a node among all the nodes in the tree.
